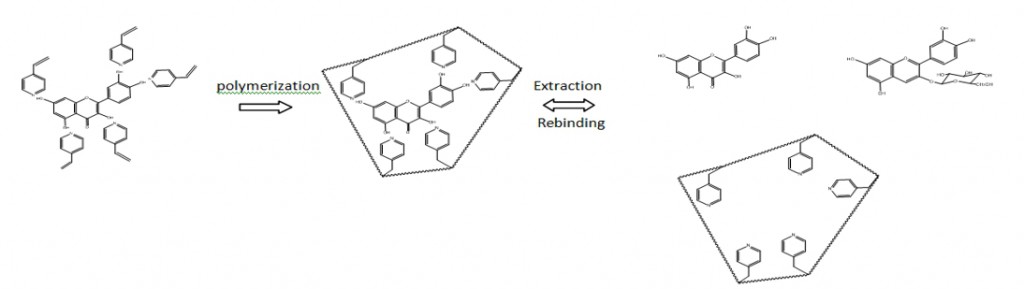
Molecular imprinting is a facilitative technology for the production of artificial receptors possessing great endurance with high specificity toward target molecules of interest. The polymers are commonly applied for separation or analysis of substances of interest. In this study, we prepared molecularly imprinted polymers for the purpose of binding specifically to quercetin and related compounds. Quercetin imprinted polymer was found to bind well against quercetin; approximately 1 mg/g polymer. In addition, QIP was applied to bind anthocyanin from the crude extract of mangosteen pericarp. The binding capacity of quercetin-IP toward anthocyanin wasapproximately 0.875 mg per g of polymer. This result indicated that quercetin-IP showed its specific binding to quercetin and related compound particularly anthocyanin. In conclusion, we have demonstrated the successful preparation and utilization of molecularly imprinted polymer for the specific recognition of quercetin as well as structurally related anthocyanins from the mangosteen pericarp with enhanced and robust performance

Unpolished Thai Rice Prevent Colorectal Cancer
January 30, 2017
Anti-Drowsy Driving Alarm (Alertz)
January 30, 2017Quercetin-imprinted polymer for Anthocyanin extraction from mangosteen pericarp
Provider : ผศ.ดร.ธีรพล เปียฉ่ำ คณะเทคนิคการแพทย์

